Plant-Based Power: Supporting Your Heart Health with Plants First
- 2/24/25
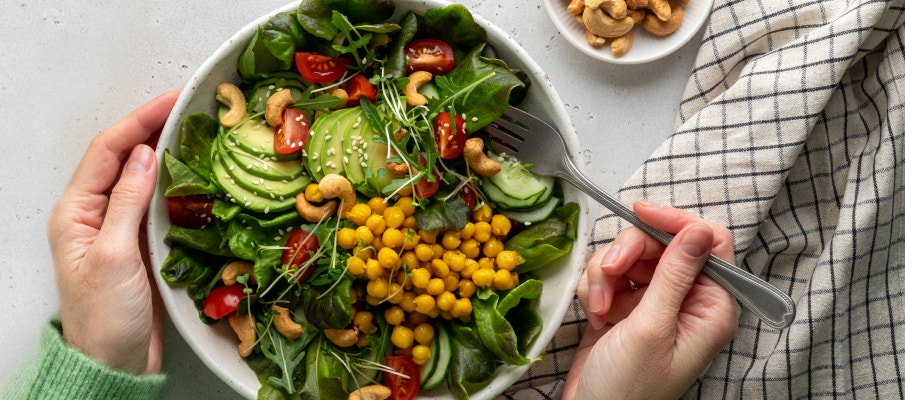


Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of death around the world, so taking good care of your heart is a top priority. Fortunately, everyday habits add up over time and your diet pattern makes a significant difference.
A plant-based diet, rich in nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains has been shown to support heart health by supporting healthy cholesterol and blood pressure and a healthy inflammatory response.
Here’s why plant foods are so good for your heart and some tips to enjoy their benefits.
Why a Plant-Based Diet is Good for Your Heart
There are several variations of a plant-based diet, which depend on your personal preferences. However, the basic premise is a diet pattern based on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, restricting or excluding animal products, such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, and eggs.
To reap the most health benefits from a plant-based diet, it’s important to prioritize whole and minimally processed foods. While it’s nice to have so many meat analogs and vegan dessert foods, for example, these tend to offer less overall nutritional quality and are best included on occasion.
Eating more plant foods is a powerful way to support your heart health because, when done right, it’s packed with essential nutrients and low in saturated fat.
In addition to vitamins and minerals, plants contain antioxidants, which are compounds that protect your cells from oxidative stress and damage that promotes disease. They’re also the only natural source of fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol and support healthy arteries.
Key Components of a Heart-Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet focuses on nutrient-dense foods that support healthy heart function.
While avoiding dietary components like high-sodium foods, saturated fat, and added sugars, heart-healthy diets also prioritize a variety of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants—which are easy to find in a plant-based diet.
Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice are rich in soluble fiber, known for lowering LDL cholesterol. Legumes, nuts, and seeds offer plant-based proteins, healthy fats, and essential nutrients like magnesium and potassium that support heart health. Healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and flaxseeds help improve blood fats.
By prioritizing these nutritious, versatile foods, a heart-healthy diet lays the foundation for long-term cardiovascular wellness.
Tips for Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Like any change to your diet pattern, going plant-based can involve some trial and error. Here are some tips to help make it a smoother transition:
- Start small: Begin with one plant-based meal per day or try Meatless Mondays to ease into the transition.
- Focus on what you can add: Add more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to your meals rather than focusing on what to cut out.
- Explore plant proteins: Incorporate lentils, beans, tofu, and tempeh to ensure balanced and satiating meals.
- Experiment with flavors: Use herbs, spices, and plant-based sauces to enhance the taste and variety of your dishes.
- Consider supplements: Use high-quality plant-based supplements to fill potential nutrient gaps. Vitamin B12 is essential for plant-based eaters, our Vitamin B12 Organic Raspberry Spray is a tasty option to consider. You may also want to consider an omega-3 supplement, like our Vegan DHA soft gels derived from algae, as well as a vitamin D supplement if your blood levels are low. Our Vegan Raspberry Lemon chewables provide 2,000 IU per serving. For personalized supplement recommendations, you should consult with a plant-based registered dietitian.
Your Heart on Plants: Final Thoughts
A plant-based diet is a proven way to support your heart and overall wellness. Plant foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support healthier cholesterol levels, blood sugar regulation, and healthy inflammatory response. Incorporating more plants into your diet and supplementing where appropriate can be a huge step toward better heart health.
Curious about other heart-healthy supplements that may complement a plant-based diet? Check out our line of products designed to support a healthy heart and overall wellness
Sources
- Trautwein EA, McKay S. The Role of Specific Components of a Plant-Based Diet in Management of Dyslipidemia and the Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients. 2020 Sep 1;12(9):2671. doi: 10.3390/nu12092671. PMID: 32883047; PMCID: PMC7551487.
- Joshi S, Ettinger L, Liebman SE. Plant-Based Diets and Hypertension. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2019 Sep 24;14(4):397-405. doi: 10.1177/1559827619875411. PMID: 33281520; PMCID: PMC7692016.
- McMacken M, Shah S. A plant-based diet for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2017 May;14(5):342-354. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.05.009. PMID: 28630614; PMCID: PMC5466941.
- Escalante-Araiza F, Rivera-Monroy G, Loza-López CE, Gutiérrez-Salmeán G. The effect of plant-based diets on meta-inflammation and associated cardiometabolic disorders: a review. Nutr Rev. 2022 Aug 8;80(9):2017-2028. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuac020. PMID: 35475468.
- Salehin S, Rasmussen P, Mai S, Mushtaq M, Agarwal M, Hasan SM, Salehin S, Raja M, Gilani S, Khalife WI. Plant Based Diet and Its Effect on Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 14;20(4):3337. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043337. PMID: 36834032; PMCID: PMC9963093.
- Greger M. A Whole Food Plant-Based Diet Is Effective for Weight Loss: The Evidence. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2020 Apr 3;14(5):500-510. doi: 10.1177/1559827620912400. PMID: 32922235; PMCID: PMC7444011.
- Whitehead A, Beck EJ, Tosh S, Wolever TM. Cholesterol-lowering effects of oat β-glucan: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;100(6):1413-21. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.086108. Epub 2014 Oct 15. PMID: 25411276; PMCID: PMC5394769.
- Mullins AP, Arjmandi BH. Health Benefits of Plant-Based Nutrition: Focus on Beans in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nutrients. 2021 Feb 5;13(2):519. doi: 10.3390/nu13020519. PMID: 33562498; PMCID: PMC7915747.
- Craig WJ, Mangels AR, Fresán U, Marsh K, Miles FL, Saunders AV, Haddad EH, Heskey CE, Johnston P, Larson-Meyer E, Orlich M. The Safe and Effective Use of Plant-Based Diets with Guidelines for Health Professionals. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 19;13(11):4144. doi: 10.3390/nu13114144. PMID: 34836399; PMCID: PMC8623061.