The Benefits of Prebiotics
- 4/17/23
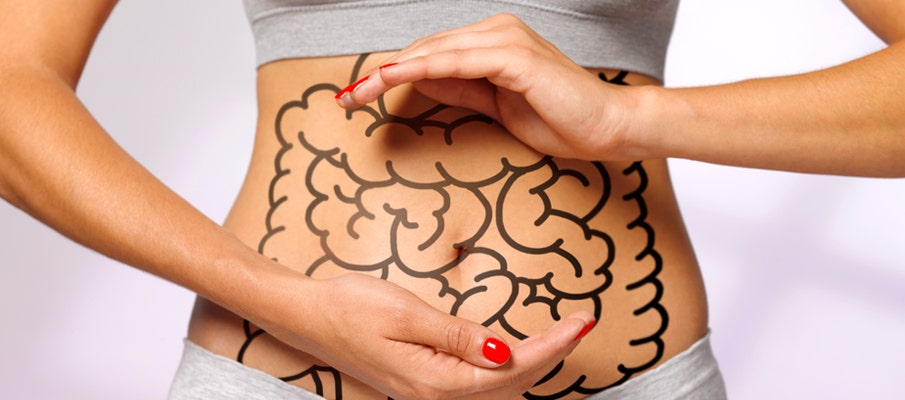


Probiotics have gained much attention in the world of gastrointestinal health. However, prebiotics also play an important role in maintaining a healthy gut.
While probiotics, the healthy bacteria found within your gut, can help promote gut health, prebiotics provide food for the healthy bacteria in your gut, allowing them to flourish and grow.
Let’s take a closer look at prebiotics, where they can be found, and how they can support the health of your gut and overall well-being.
What Are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are indigestible natural fibers, typically found in various complex carbohydrates. These indigestible fibers circumvent your small intestine and enter your colon where they are fermented. During this fermentation process, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that have been linked to improved digestive health.
While your body can’t digest prebiotics, the healthy bacteria in your gut can. Therefore, prebiotics act as food for healthy gut bacteria, helping to stimulate the growth of good probiotic bacteria within your gut while hindering the growth of harmful bacteria.
Prebiotics work with probiotics to help maintain the balance of bacteria and to help support the diversity of helpful bacteria within your gut.† As a result, prebiotics are often taken to maximize the benefits of probiotics.
Where Can Prebiotics Be Found?
Prebiotics naturally exist in some foods and can also be found in supplement form. Some prebiotic foods to consider incorporating into your diet include:
- Asparagus
- Onion
- Garlic
- Whole grains
- Tomato
- Oats
- Peas
- Lentils
- Bananas
If you’re eating a wide variety of fiber-rich foods daily, you may be naturally consuming adequate amounts of prebiotic fiber. However, recent observational studies have shown that only 5% of Americans consume sufficient amounts of dietary fiber each day. Therefore, you may consider taking a prebiotic supplement to optimize your gut health.
Many supplements known as "synbiotics" will provide both probiotics and prebiotics to further support gut health. Common names for prebiotics in supplements may include resistant starch, fructans, including inulin and fructooligosaccharides, and galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS).
Choosing a supplement made from actual food may increase the bioavailability of the nutrient, meaning it will be more easily absorbed by your body. Additionally, choosing a supplement that offers a variety of fibers may further support the growth of beneficial bacteria within your gut microbiome.
Potential Health Benefits of Prebiotics
Prebiotics have been linked to a wide range of health benefits, as research shows they may help support healthy digestion, immunity, and a healthy weight.†
Supports Healthy Digestion†
If you’re looking for a way to experience more regular bowel movements, prebiotics may help. In one recent review, prebiotics helped to improve stool consistency, reduce bloating, and increase the number of bowel movements in adults.†
Another study examined the effect of the prebiotic inulin on the regulation of bowel movements. Researchers found that inulin helped to regulate bowel transit time and the consistency and frequency of the stools by way of the improved composition of the gut microbiome.†
Supports a Healthy Immune System†
Your microbiome plays a significant role in supporting a healthy immune system. A growing body of research suggests that prebiotics support healthy immunity by helping to increase the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) which play an important role in immune cell production.†
Supports a Healthy Weight†
Recent studies indicate that there may be a link between an imbalanced gut microbiome and ghrelin, the "hunger hormone" that stimulates your appetite and increases food intake. Researchers found that taking synbiotics (probiotics with prebiotics) can help increase satiety and may support a healthy weight.†
The Bottom Line
Prebiotics are dietary fibers that help support probiotics by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut microbiome. These important dietary fibers can be found in a variety of food sources. However, many people may not be getting the recommended amount of fiber and therefore may need a prebiotic supplement for support.†
The health benefits of prebiotics include supporting healthy digestion, immune functioning, and supporting a healthy weight. If you’re looking for improved digestive health along with other benefits, you may consider taking "synbiotics", which provide both probiotics and prebiotics to further support your health and overall wellbeing.†
†These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
References:
-
Pedro Gonçalves, PhD, João Ricardo Araújo, PhD, James P Di Santo, MD, PhD, A Cross-Talk Between Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids and the Host Mucosal Immune System Regulates Intestinal Homeostasis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Volume 24, Issue 3, March 2018, Pages 558–572, https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izx029
-
Davani-Davari D, Negahdaripour M, Karimzadeh I, Seifan M, Mohkam M, Masoumi SJ, Berenjian A, Ghasemi Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods. 2019 Mar 9;8(3):92. doi: 10.3390/foods8030092. PMID: 30857316; PMCID: PMC6463098.
-
Ioniță-Mîndrican C-B, Ziani K, Mititelu M, Oprea E, Neacșu SM, Moroșan E, Dumitrescu D-E, Roșca AC, Drăgănescu D, Negrei C. Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients. 2022; 14(13):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132641
-
Naseer M, Poola S, Uraz S, Tahan V. Therapeutic Effects of Prebiotics on Constipation: A Schematic Review. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2020;15(3):207-215. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666200212125035. PMID: 32048977.
-
Bărboi OB, Ciortescu I, Chirilă I, Anton C, Drug V. Effect of inulin in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2020 Dec;20(6):185. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9315. Epub 2020 Oct 13. PMID: 33101475; PMCID: PMC7579772.
-
Pujari R, Banerjee G. Impact of prebiotics on immune response: from the bench to the clinic. Immunol Cell Biol. 2021 Mar;99(3):255-273. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12409. Epub 2020 Nov 2. PMID: 32996638.
-
Álvarez-Arraño V, Martín-Peláez S. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 17;13(10):3627. doi: 10.3390/nu13103627. PMID: 34684633; PMCID: PMC8540110.