Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Acid Indigestion
- 4/15/19

by Ashley Grano
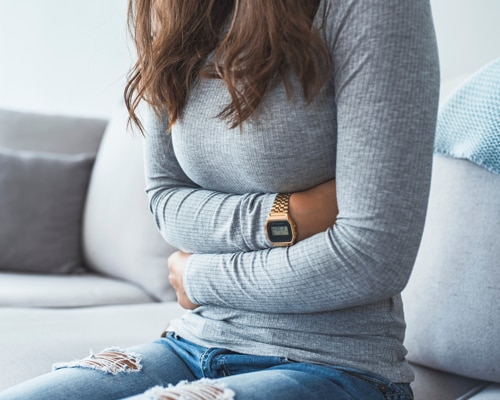
Nearly everyone has experienced an episode of acid indigestion, which is usually described as an uncomfortable, burning pain that often begins in the stomach and goes up into the chest and throat. This may be accompanied by a sour, bitter taste, as acid backs up into the throat.
In most cases, the cause of acid indigestion can be easily attributed to a situational factor, like consuming a high-fat, heavy meal late at night or eating too quickly. However, heartburn and indigestion can also be symptoms of acid reflux disease, which can lead to some serious health implications if left untreated. When acid indigestion becomes persistent, it is important to rule out underlying causes and seek treatment.
What is acid reflux, and why should you be concerned about it?
Acid reflux issues are quite prevalent, with over 60 million Americans experiencing symptoms at least once monthly, according to WebMD. Acid reflux disease is also commonly referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, GERD is technically the more severe form of acid reflux, says the Mayo Clinic. Acid reflux is defined as the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus. It commonly causes symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and dyspepsia. Difficulty swallowing, stomach fullness, burping, nausea, sore throat, and dry cough may also be symptoms, reports Healthline.
As a common disorder, many people don’t take the condition seriously until symptoms become very severe or persistent. Mild symptoms can be relatively easy to treat with OTC medications, which can dissuade sufferers from seeking proper professional medical attention. However, even mild symptoms of acid reflux may be warning signs that stomach acid has inflamed the esophagus, explains WebMD. In time, this can lead to damage and bleeding, which can even lead to cancer.
In addition, symptoms of indigestion often signal underlying health issues, such as ulcers, heart disease, hiatal hernia, gallbladder disease, and more. GERD can also be caused by a damaged or weakened lower esophageal sphincter, says Healthline. Therefore, since there can be many reasons for the development of acid indigestion issues, early treatment is best to pinpoint the cause and avoid greater health complications.
How diet modifications can help with acid indigestion issues
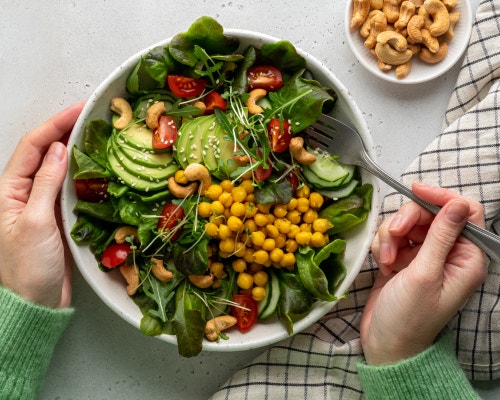
Following a healthy diet can go a long way in improving acid indigestion issues. For people who produce too much stomach acid, adding certain foods into the diet can help mitigate symptoms, Healthline suggests. Leafy greens, broccoli, and asparagus are great vegetable choices that can help lower stomach acid. Oatmeal is a high-fiber food that is ideal for absorbing excess stomach acid. Healthy fats like avocados, walnuts, flax, and olive oil are also good for avoiding acid indigestion while helping to feel full. Adding sliced or grated ginger into a drink or smoothie can settle an upset stomach.
Foods to avoid include egg yolks, tomatoes, citrus fruits, high-fat, greasy and fried foods, processed meats, full-fat dairy, and heavy creams and sauces. Spicy seasonings as well as garlic and onions are also often best avoided, although they may be tolerated by some people. Unfortunately, even chocolate and caffeine can be potential GERD triggers, and should be limited. Experts suggest keeping a food diary to keep track of problematic foods.
In addition to what types of foods are consumed, how they are consumed is also important to help prevent heartburn and symptoms of acid indigestion. WebMD suggests eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day, such as 5-6 smaller meals as compared to 3 large meals. In addition, avoid eating and then going to lie down immediately after. Allow the body to digest food for at least two to three hours before bedtime.
Avoiding other acid ingestion triggers
Exercise habits can also contribute to acid indigestion. Rigorous activities like running or strenuous aerobics like HIIT training can lead to discomfort in people with a weakened lower esophageal sphincter, says WebMD. Some abdominal-intensive exercises can also stress people sensitive to heartburn. Always be sure to wait at least two hours after eating before beginning any exercise routine.
Certain medications can trigger heartburn and symptoms of acid reflux, including anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), some blood pressure medications, antidepressants, birth control pills, sedatives, and even various supplements, reports WebMD.
Acid reflux and GERD can also be managed by lifestyle changes such as losing weight (if overweight) and quitting smoking, suggests the Cleveland Clinic.
Nearly everyone has experienced an episode of acid indigestion, which is usually described as an uncomfortable, burning pain that often begins in the stomach and goes up into the chest and throat. This may be accompanied by a sour, bitter taste, as acid backs up into the throat.
In most cases, the cause of acid indigestion can be easily attributed to a situational factor, like consuming a high-fat, heavy meal late at night or eating too quickly. However, heartburn and indigestion can also be symptoms of acid reflux disease, which can lead to some serious health implications if left untreated. When acid indigestion becomes persistent, it is important to rule out underlying causes and seek treatment.
What is acid reflux, and why should you be concerned about it?
Acid reflux issues are quite prevalent, with over 60 million Americans experiencing symptoms at least once monthly, according to WebMD. Acid reflux disease is also commonly referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, GERD is technically the more severe form of acid reflux, says the Mayo Clinic. Acid reflux is defined as the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus. It commonly causes symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and dyspepsia. Difficulty swallowing, stomach fullness, burping, nausea, sore throat, and dry cough may also be symptoms, reports Healthline.
As a common disorder, many people don’t take the condition seriously until symptoms become very severe or persistent. Mild symptoms can be relatively easy to treat with OTC medications, which can dissuade sufferers from seeking proper professional medical attention. However, even mild symptoms of acid reflux may be warning signs that stomach acid has inflamed the esophagus, explains WebMD. In time, this can lead to damage and bleeding, which can even lead to cancer.
In addition, symptoms of indigestion often signal underlying health issues, such as ulcers, heart disease, hiatal hernia, gallbladder disease, and more. GERD can also be caused by a damaged or weakened lower esophageal sphincter, says Healthline. Therefore, since there can be many reasons for the development of acid indigestion issues, early treatment is best to pinpoint the cause and avoid greater health complications.
How diet modifications can help with acid indigestion issues
Following a healthy diet can go a long way in improving acid indigestion issues. For people who produce too much stomach acid, adding certain foods into the diet can help mitigate symptoms, Healthline suggests. Leafy greens, broccoli, and asparagus are great vegetable choices that can help lower stomach acid. Oatmeal is a high-fiber food that is ideal for absorbing excess stomach acid. Healthy fats like avocados, walnuts, flax, and olive oil are also good for avoiding acid indigestion while helping to feel full. Adding sliced or grated ginger into a drink or smoothie can settle an upset stomach.
Foods to avoid include egg yolks, tomatoes, citrus fruits, high-fat, greasy and fried foods, processed meats, full-fat dairy, and heavy creams and sauces. Spicy seasonings as well as garlic and onions are also often best avoided, although they may be tolerated by some people. Unfortunately, even chocolate and caffeine can be potential GERD triggers, and should be limited. Experts suggest keeping a food diary to keep track of problematic foods.
In addition to what types of foods are consumed, how they are consumed is also important to help prevent heartburn and symptoms of acid indigestion. WebMD suggests eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day, such as 5-6 smaller meals as compared to 3 large meals. In addition, avoid eating and then going to lie down immediately after. Allow the body to digest food for at least two to three hours before bedtime.
Avoiding other acid ingestion triggers
Exercise habits can also contribute to acid indigestion. Rigorous activities like running or strenuous aerobics like HIIT training can lead to discomfort in people with a weakened lower esophageal sphincter, says WebMD. Some abdominal-intensive exercises can also stress people sensitive to heartburn. Always be sure to wait at least two hours after eating before beginning any exercise routine.
Certain medications can trigger heartburn and symptoms of acid reflux, including anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), some blood pressure medications, antidepressants, birth control pills, sedatives, and even various supplements, reports WebMD.
Acid reflux and GERD can also be managed by lifestyle changes such as losing weight (if overweight) and quitting smoking, suggests the Cleveland Clinic.