Tag-Team Exercise
- 12/16/15

When you exercise, there are two basic types: aerobic and anaerobic. And you need both to tag team your fitness level.
Aerobic exercise causes the body to utilize oxygen to create energy—basically, anything that gets the heart going, such as walking on treadmills, cycling on stationary bikes or stepping on stair stepper machines. Aerobic exercise is generally associated with non-resistance exercises.
Other forms of aerobic exercise include golfing, soccer, tennis, walking, basketball, hiking, volleyball, softball and dancing. In general, aerobic exercise is performed at a low- to moderate-intensity level. In fact, you’re said to be exercising aerobically if you can pass the “talk test,” meaning you can carry on a conversation and exercise at the same time.
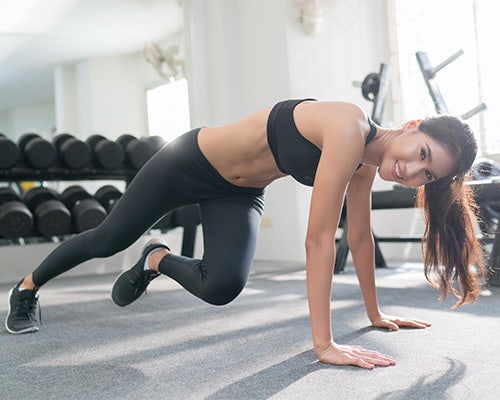
On the other hand, anaerobic exercise is any form of non-sustained physical activity that typically involves a limited number of specific muscles over a short time, such as strength training or lifting free weights. You work the body anaerobically when the cardiovascular capacity cannot replenish the muscles with energy—and you’re so out of breath that you can’t pass the “talk test.” In fact, a good marker to see if you’re in the anaerobic zone during your workout—where you’re strengthening your heart and lungs—is the fact that you’re panting and sweating between each set.
Examples of anaerobic exercise are: lifting weights, using strength machines, jumping rope or jumping on a rebounder, sprinting, or working the body’s core muscles with resistance bands, stability balls, medicine balls or kettlebells.
We need both aerobic and anaerobic exercise for optimal physical benefits.
How about you? Are you tag-teaming your exercise regimen?
In order to avoid risk of injury, please seek advice directly from your physician, especially if you have existing medical issues, before beginning any exercise or nutritional program. Also, be sure to stretch after exercise to avoid muscle and joint tightness.
This information is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It should not be used in place of an individual consultation or examination or replace the advice of your health care professional and should not be relied upon to determine diagnosis or course of treatment.
Aerobic exercise causes the body to utilize oxygen to create energy—basically, anything that gets the heart going, such as walking on treadmills, cycling on stationary bikes or stepping on stair stepper machines. Aerobic exercise is generally associated with non-resistance exercises.
Other forms of aerobic exercise include golfing, soccer, tennis, walking, basketball, hiking, volleyball, softball and dancing. In general, aerobic exercise is performed at a low- to moderate-intensity level. In fact, you’re said to be exercising aerobically if you can pass the “talk test,” meaning you can carry on a conversation and exercise at the same time.
On the other hand, anaerobic exercise is any form of non-sustained physical activity that typically involves a limited number of specific muscles over a short time, such as strength training or lifting free weights. You work the body anaerobically when the cardiovascular capacity cannot replenish the muscles with energy—and you’re so out of breath that you can’t pass the “talk test.” In fact, a good marker to see if you’re in the anaerobic zone during your workout—where you’re strengthening your heart and lungs—is the fact that you’re panting and sweating between each set.
Examples of anaerobic exercise are: lifting weights, using strength machines, jumping rope or jumping on a rebounder, sprinting, or working the body’s core muscles with resistance bands, stability balls, medicine balls or kettlebells.
We need both aerobic and anaerobic exercise for optimal physical benefits.
How about you? Are you tag-teaming your exercise regimen?
In order to avoid risk of injury, please seek advice directly from your physician, especially if you have existing medical issues, before beginning any exercise or nutritional program. Also, be sure to stretch after exercise to avoid muscle and joint tightness.
This information is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It should not be used in place of an individual consultation or examination or replace the advice of your health care professional and should not be relied upon to determine diagnosis or course of treatment.